Symptoms of lung fibrosis, a progressive scarring of lung tissue, can range from subtle to severe, impacting breathing and overall well-being. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of this debilitating condition.
Definition and Overview
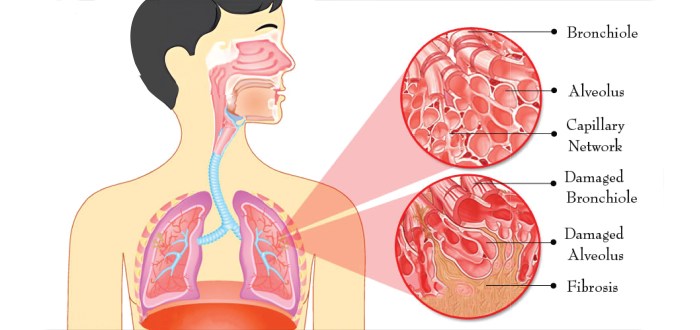
Lung fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred and thickened, making it difficult to breathe. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to certain toxins, autoimmune diseases, and radiation therapy.Lung fibrosis is a serious condition that can lead to disability and death.
There is no cure for lung fibrosis, but there are treatments that can help to slow the progression of the disease and improve symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of lung fibrosis is unknown, but there are a number of risk factors that have been identified, including:* Exposure to certain toxins, such as asbestos, silica, and coal dust
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
- Radiation therapy
- Certain medications, such as methotrexate and amiodarone
- Smoking
- Age
- Family history of lung fibrosis
Symptoms and Signs: Symptoms Of Lung Fibrosis
Lung fibrosis is a progressive disease, meaning that the symptoms tend to worsen over time. The rate of progression varies from person to person and depends on the type of lung fibrosis.
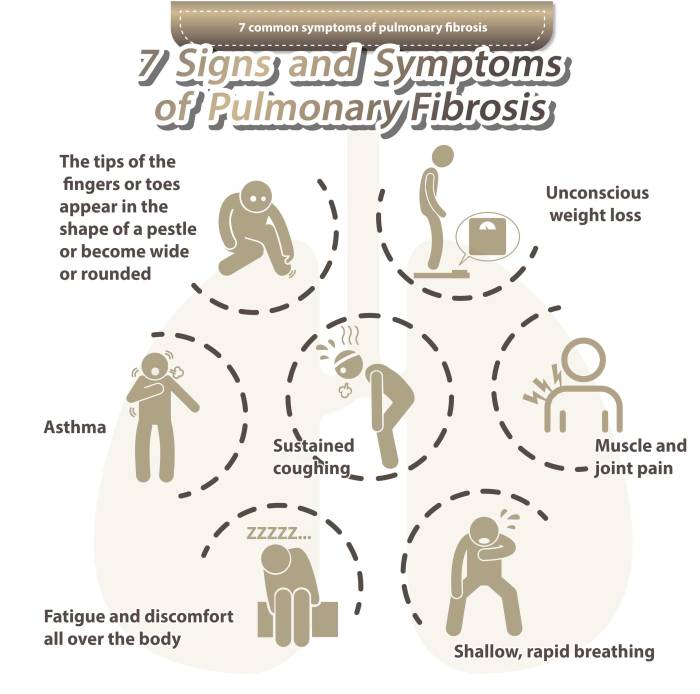
The most common symptoms of lung fibrosis include:
- Shortness of breath, especially with exertion
- A dry, hacking cough that may or may not produce mucus
- Fatigue
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
The severity of the symptoms can vary depending on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, people may only experience mild shortness of breath with exertion. As the disease progresses, the symptoms can become more severe and may include shortness of breath at rest, difficulty breathing while lying down, and a persistent cough.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing lung fibrosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Imaging techniques like chest X-rays and CT scans help visualize lung abnormalities, while lung biopsies provide definitive confirmation of the condition.
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are crucial in assessing lung function and monitoring disease progression. These tests measure lung volume, airflow, and gas exchange, providing valuable insights into the severity and extent of lung fibrosis.
Imaging Techniques
- Chest X-rays:Initial screening tool that can reveal characteristic lung changes associated with fibrosis, such as reticular opacities and honeycombing.
- CT scans:More detailed imaging technique that provides cross-sectional views of the lungs, allowing for better visualization of fibrotic lesions and lung architecture.
Lung Biopsy
Lung biopsy involves removing a small sample of lung tissue for examination under a microscope. This definitive diagnostic procedure can confirm the presence and type of lung fibrosis.
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
PFTs are a group of tests that assess lung function by measuring various parameters, including:
- Lung volume
- Airflow
- Gas exchange
These tests help determine the severity of lung fibrosis and monitor its progression over time.
Treatment Options
Lung fibrosis is a chronic and progressive disease, and there is no cure. However, there are a number of treatment options available that can help to slow the progression of the disease and improve symptoms.
The goals of treatment for lung fibrosis include:
- Slowing the progression of the disease
- Improving symptoms
- Improving quality of life
The type of treatment that is recommended for a particular patient will depend on the severity of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and the patient’s preferences.
Medications
There are a number of medications that can be used to treat lung fibrosis. These medications include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Immunosuppressants
- Anti-fibrotic medications
Anti-inflammatory medications can help to reduce inflammation in the lungs. Immunosuppressants can help to suppress the immune system, which can slow the progression of the disease. Anti-fibrotic medications can help to prevent the formation of scar tissue in the lungs.
Oxygen Therapy, Symptoms of lung fibrosis
Oxygen therapy can help to improve the amount of oxygen in the blood. This can help to relieve shortness of breath and improve exercise tolerance.
Lung Transplantation
Lung transplantation is a surgical procedure in which the diseased lungs are replaced with healthy lungs from a donor. Lung transplantation is a major surgery, but it can be a life-saving procedure for patients with severe lung fibrosis.
Complications and Prognosis
Lung fibrosis can lead to several serious complications that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and overall health.
One of the most common complications of lung fibrosis is respiratory failure. This occurs when the lungs are unable to adequately exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood and a decrease in blood oxygen levels.
Respiratory failure can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Heart Failure
Lung fibrosis can also lead to heart failure. This occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can be caused by the increased pressure in the lungs, which makes it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Heart failure can lead to a number of symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles.
Pulmonary Hypertension
Another potential complication of lung fibrosis is pulmonary hypertension. This occurs when the pressure in the arteries that carry blood from the heart to the lungs becomes too high. This can lead to a number of symptoms, including shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue.
Pulmonary hypertension can also damage the heart and lead to heart failure.
Prognosis
The prognosis for lung fibrosis varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some types of lung fibrosis are more aggressive than others, and the prognosis can be worse for people who have more severe disease. However, with early diagnosis and treatment, many people with lung fibrosis can live long and fulfilling lives.
Lifestyle Management and Prevention
Managing lung fibrosis involves adopting lifestyle modifications to alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life. Additionally, preventive measures can potentially reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Smoking Cessation:Smoking is a significant risk factor for lung fibrosis. Quitting smoking can slow disease progression and improve lung function.
- Exercise:Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, helps maintain lung capacity and reduces shortness of breath.
- Oxygen Therapy:Supplemental oxygen may be necessary to improve oxygen levels in the blood, especially during exertion or sleep.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation:This program combines exercise, education, and support to improve lung function and overall well-being.
- Nutritional Management:Maintaining a healthy weight and consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and well-being.
Preventive Measures
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent lung fibrosis, certain measures may reduce the risk:
- Avoiding Exposure to Harmful Substances:Minimizing exposure to pollutants, such as asbestos, silica, and certain chemicals, can reduce the risk of developing lung fibrosis.
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment:Prompt diagnosis and treatment of underlying conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or infections, can potentially prevent lung fibrosis from developing or progressing.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research efforts and advancements in the understanding and treatment of lung fibrosis offer hope for the future management of this condition. Researchers are actively exploring various approaches to improve diagnosis, develop more effective treatments, and ultimately find a cure for lung fibrosis.
Novel Therapies
- Anti-fibrotic medications:These medications, such as pirfenidone and nintedanib, have shown promise in slowing the progression of lung fibrosis by targeting specific pathways involved in the development of scar tissue.
- Immunomodulatory therapies:These therapies aim to modulate the immune system to reduce inflammation and fibrosis. Examples include corticosteroids, methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil.
- Stem cell therapy:Researchers are exploring the potential of stem cells to repair damaged lung tissue and promote regeneration.
- Gene therapy:This approach aims to correct or modify genetic defects that contribute to lung fibrosis.
Improved Diagnostics
- Biomarkers:Researchers are identifying biomarkers in blood, urine, or tissue samples that can help diagnose lung fibrosis earlier and more accurately.
- Imaging techniques:Advanced imaging techniques, such as high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are being refined to provide more detailed and precise images of lung tissue.
Potential Impact
These advancements have the potential to significantly improve the outlook for people with lung fibrosis. Earlier diagnosis and more effective treatments can slow the progression of the disease, preserve lung function, and enhance quality of life. In the future, it is possible that lung fibrosis may be curable or manageable as a chronic condition, allowing individuals to live longer, healthier lives.
Closing Notes
Recognizing the symptoms of lung fibrosis is the first step towards seeking timely medical attention and managing the condition effectively. By understanding the telltale signs, individuals can proactively engage in lifestyle modifications, adhere to treatment plans, and improve their quality of life.
FAQ Section
What are the common symptoms of lung fibrosis?
Shortness of breath, dry cough, fatigue, wheezing, and chest pain are common symptoms.
How is lung fibrosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical exam, chest X-ray, CT scan, lung function tests, and sometimes a lung biopsy.
Is lung fibrosis curable?
Currently, there is no cure for lung fibrosis, but treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
What are the risk factors for lung fibrosis?
Smoking, exposure to certain toxins or pollutants, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk.
How does lung fibrosis affect daily life?
It can significantly impact breathing, exercise tolerance, and overall well-being, affecting daily activities and quality of life.